Thank you ![]()
I’m taking the driver license exam. would this or emotional dampener be better to control my emotions and my heartbeat?i have about 2 weeks until then
the main point is to give to everyone a tool to help you quickly deal with unwanted experiences - to get rid of fears, phobias, sadness, etc… As quickly as possible
The main function of this field is a short-term therapy technique. It allows you to take an experience, extract energy from it and use it for peaceful purposes.
But what I understand by it doesn’t quite fit the dictionary definition. For a Russian person, “experience” is synonymous with “nervousness”, “fear”, “suffering”, and so on.
Psychologists are visited by those who have some obstacles on the way from conception to realization. a person thinks of something, but cannot realize it - it does not work out, something prevents it
Let’s imagine a person who can’t turn his idea into reality.
For example, he wants a happy relationship, but as soon as he thinks that he needs to get acquainted with girls, fear, insecurity, stiffness and thoughts of “who needs me like this?” immediately arise. This is a block - something does not allow you to move freely towards the realization of your vision.
I would call the blockage that arises on the way from conception to reality “charge”.
a person has something in mind, but when trying to realize it, something starts to interfere or distract (negative thoughts, bodily sensations, emotions or imaginary pictures).
when there is no “charge”, a person can easily move towards realization. Wanted a relationship - went to meet girls, etc.
When a person perceives something - it is not always in the accepted reality. more often on the contrary - what he perceives is only in his head. It’s probably familiar to everyone ![]()
who’s never been afraid of something that’s not present in reality at the moment? Next week’s exam, the death of his or her loved ones, or even a world catastrophe. A person doesn’t need something to be out there to worry about it - it’s enough to imagine it
there is a plus in this - we can imagine and work through something without having direct contact with the stimulus. So we don’t have to see a real rat to work through the fear of it. Nor do we have to climb on the roof of a high-rise to work on our fear of heights
but the downside is that we can be afraid of things that aren’t there. And even though it’s not there in reality, it’s just as scary. And of course from here negative thoughts, emotions, bodily sensations (heart palpitations, lump in the throat, goosebumps), etc.
That is, with the help of this audio it is possible to work with those experiences that the user calls negative or unwanted - i.e. an unwanted picture, bodily sensation, emotion and thought. These experiences can be called charged experiences. It’s as simple as that.
Just choose what works for you specifically ![]()
You did it again! I feel that these two fields are very well paired.
Private realization shared:
In relating to and perceiving ideas
Summary
So for the past several weeks subconsciously I’ve been developing some pre-cognition/deja vu, and it continues to develop. There are also ideas about aligning with a harmonious universe, and the pressure that turns stones into --higher states of consciousness. Anyway, with having glimpses of a possible future, it becomes easier to very naturally align your deepest needs/wants with what is being created & shared. That feeling of synchronicity or resonance, elevated. And then with guidance (eg. Angelic), more of inner reality (of being) mirroring with outer reality.
From which field, or both together?
Ah sorry, wasn’t clear in the writing. More on the process leading up to an event, and how one is in relation to it. Like being “prepared” with your being.
Not anything on these two fields themselves.
Good luck buddy!!
This is crazy good and powerful. Two days in and the improvements in my inner world have been outstanding already. 🥲🥲🥲🥲🥲
thanks. it’s my 2nd try. last time went really bad. when I saw the police man it triggered some fear I didn’t even know I had of them and I was super stressed and forgot everything I had to do
Anatomy of a traumatic experience
Summary
In the lives of the vast majority of people, there are bound to be some unwanted conditions, unpleasant memories, strange beliefs, and even whole failed areas of life that we would like to resolve, correct, and live to our satisfaction
Most of our limitations, disabilities and undesirable states are the consequences of some event in the past, usually unpleasant, which are called “traumatic experiences”
few people consciously follow a particular path in life. Usually, there is a certain channel along which life flows. This course has boundaries - a corridor of comfort - a set of all possible variants of events that fit within the framework of expectations, when it is known what to do and how to react.
as long as everything happens within this corridor of comfort and does not go beyond the known deviations, a person feels more or less well. There is some template reaction to any situation that occurs, he copes, feels successful and moves along some vector in this comfort zone
sometimes, of course, something happens that is not exactly as we would like it to be, but if the differences are not painful, but just unpleasant, it is not a traumatic experience.
If I wake up in the morning hoping for good weather, but it is raining outside the window, it can hardly be called a psychological trauma. ![]()
when a person follows this path of life, it is unlikely that he or she is acutely aware of his or her needs. If these needs are not violated, he feels more or less normal, but he cannot learn any lessons from life.
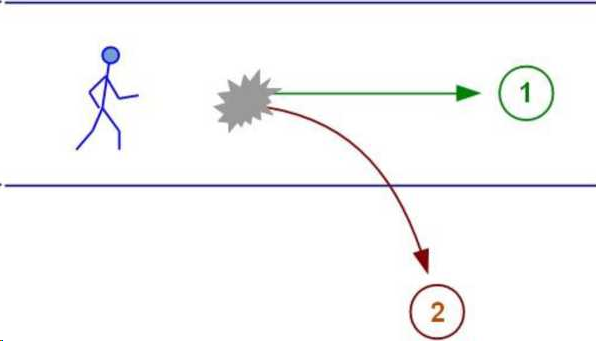
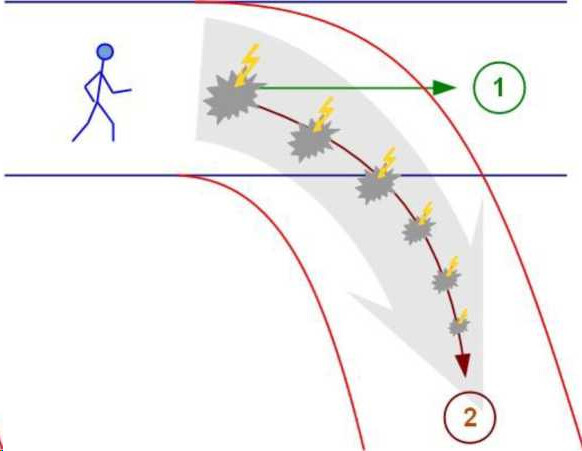
the diagram below shows this corridor of comfort and a man walking briskly along it. If everything is normal, he will come to the point marked with the number 1. That is where his comfort corridor leads him
if an event occurs in which a person does not understand what to do, if he does not have a prepared pattern of behavior, if he has not yet encountered such a phenomenon in his life - confusion and stupor arise
there lives a man X. He has some deep needs, but there are no special conflicts in his life, he is more or less satisfied, and therefore he has never thought about what these needs are
one of the deep needs of person X is the need for a real friend; and he has a friend Y, their relations are good, they are satisfied with each other. One morning, person X goes to visit person Y, goes to the door, presses the bell button… Person X expects his friend to open the door, say, “Oh, it’s good to see you! Come on in!”, or something similar within the comfort zone
Suddenly the door opens, and person Y shows up and says, "Oh my God, there’s that asshole again! “Get the fuck out of here, why are you bothering me?”. And the door slams shut ![]()
Suddenly in the life of person X there is a situation that is very much out of his comfort zone (in the figure it is marked with number 2). Something happens that sharply and painfully differs from his expectations - a “rupture” occurs. This gap in the diagram can be seen as the distance between point 1 (where person X intended to come to) and point 2, where he actually got there
This difference is painful because a deep need is affected, the situation is not clear to person X at all, he does not have a ready-made pattern of reaction - person X is confused: he does not know what to do
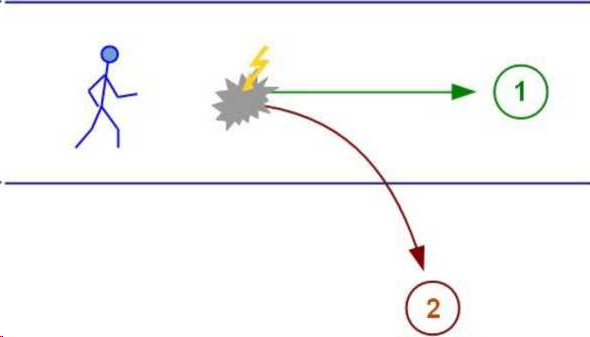
In the picture, confusion is indicated by a gray angular spot. At this moment there is an imprinted vulnerability: there is no ready pattern of response, but something must be done, something must be done somehow!
The state of confusion is extremely unpleasant, and it is necessary to get out of it as quickly as possible. To do this, you need to make a decision yourself or copy it from someone else. Such a decision that will relieve you of the suffering caused by the rupture. At the same time the recording mode is switched on: the subconsciousness needs to memorize how to get out of this situation in order to use this decision in similar cases in the future
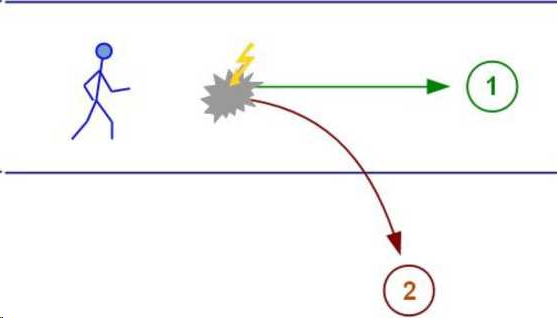
and so the person stands, looks at the slammed door and says to himself: “What a fool, eh!”, and leaves. It would seem that nothing much has happened. But person X has just made a judgment that his friend Y is a fool. In the figure, this judgment is indicated by a yellow lightning bolt
At that moment, this judgment helped to get out of the confusion.
Maybe the next day it will turn out that person Y had some problems, was not himself and did not recognize his friend at all, the situation will somehow be resolved…
But person X has already had a traumatic experience, which contains confusion and a related judgment that resolved this confusion: if person Y is a fool - then everything is clear, fools behave like that. ![]()
most likely, their friendship will fall apart sooner or later, and the deep need of a person X to have a true friend will remain in a state of chronic dissatisfaction
at the moment when a person is confused, his ancient protective system records all the circumstances of this incident and labels them as “unpleasant”. So, from nature’s point of view, one should try to avoid those circumstances
Suppose person Y had a green door. And one day person X finds that in places where there is a green door, for some reason he becomes uncomfortable. The safety reflex works in advance: green door - uncomfortable - let’s get out of here
Or person X meets a person who looks and manners are similar to person Y, and person X immediately has a feeling that this person is some kind of a… fool, for some reason. ![]()
Another example.
Girl Z is friends with boy X, they are in love, and girl Z has quite definite ideas about how it should be. One day she happily runs to her boy X, rings the doorbell, and he opens the door and says: “What are you doing here? Get out of here! I don’t want to see you anymore!”.
Girl Z is shocked - you can’t do that! She goes home, sits in the kitchen and cries. At this moment, girl Z has an imprinted vulnerability: it is not clear what happened, there is no appropriate response pattern, she needs a solution.
And then a kind mother comes in, asks what happened, and says: “Why are you crying, all men are assholes, they all want the same thing”.
О! That solves the problem! If all men are assholes, then they can act like it. The confusion is resolved, the situation is no longer so traumatic -
because now it makes sense ![]()
In a state of confusion, imprinted vulnerability, the main thing is to save oneself, to do something urgently - that is why one often takes the first solution that comes along, any solution that can be relied on and somehow get out of the situation. And then this decision is used as a template in all similar situations
man is a social creature, and in confusion he tends to accept attitudes from an external source. A person gets confused, someone says something nearby and it sticks. And it turns out that a momentary benefit seems to be received, but long-term damage is done
What will cause confusion and what will not is a subjective matter. The same event will cause confusion for one person and not for another - it all depends on the “width” of the individual corridor of comfort. ![]()
How would events develop if person X was a very flexible person and his comfort zone was large?
the person came to friend Y, and the friend said to him: “What are you doing here? Go to hell!” and slams the door shut.
Person X thinks: “He must have something wrong, he doesn’t usually behave like this”.
person X goes to his neighbor and asks: “What’s wrong with person Y?” The neighbor says: “Yes, he was dumped yesterday by his friend girl Z, he’s been angry for 24 hours.”
Man X, like a true friend, buys beer and everything that goes with beer, rings the doorbell again, and when man Y comes out, stands up so that he has no time to slam the door and says: “Let’s not do that! Let’s sit down, have a beer, talk it over…”
what’s the difference? This person X has a template for how to solve such a problem, while the previous version of person X had no such template ![]()
A traumatic experience consists of three elements:
1. A sharp painful mismatch between what happened and what the person was expecting, consciously or not.
2. Confusion or pattern breaking occurs, and the person enters a state of imprinted vulnerability.
3. A certain attitude is adopted that resolves the situation at that time.
Most traumatic experiences occur in childhood, and this is when patterns of behavior in different situations are formed.
Some of these patterns we subconsciously borrow from our parents, when in moments of confusion they said: "this is so, because...".
We unconsciously repeat these patterns, and then we cannot change them - because in order to change a pattern, we need to remember the original episode, to describe: where, what, when, with whom it happened, what were the feelings, needs and what decision was made that "resolved" the situation.
It is often very difficult to find out what kind of belief was adopted. The case when girl Z comes home, cries, her mom tells her: “all men are assholes, you can’t trust them”, and girl Z accepts it - very simple, this belief is easy to get. There are much more situations when the decision is taken something like this:
And every time, when you find yourself in a similar situation, this specific feeling arises - it is uncomfortable, and a person tries to avoid both the feeling itself and the situation in which it arises.
This decision is made at the level of bodily sensations, without participation of the conscious part of the brain, and it has no name, it is not formulated in words. In order to analyze this decision, it is necessary to replay the episodes connected with it, to remember what happened, what were the feelings, sensations, needs - in order to realize the decision and formulate it ![]()
The theory of karma from a psychological point of view
Summary
a person gets into a traumatic experience and in a state of confusion makes a decision. Most often it is made unconsciously, this decision is blocked by charges, the person does not want to look there, it is unpleasant. And then this decision starts to work as a defense mechanism, which is triggered every time there are some signs of the initial traumatic situation.
and since the mechanism is a defense mechanism, its purpose is not to reproduce what happened the first time, but to prevent it from happening again. To trigger the mechanism, it is enough to see just one sign of the original situation, and if there is no repetition of the original episode - for whatever reason - it is concluded that the defense mechanism rescued.
This results in secondary experiences that only confirm the decision made.
the deep need of person X to have a real friend has not gone anywhere, but now the intention to have a real friend has a small amendment in the form of a defense mechanism: “he is a fool, you can’t trust him”. And every time person X tries to make a real friend, sooner or later something happens that turns on this defense mechanism.
For example, person X came to a new friend Y2, and he did not open the door simply because he was not at home. But the defense mechanism tells person X: “Fool!”.
We see that, over time, an accidentally made decision turns into a belief, which is extremely difficult to work through: after all, it is not just a belief, it is backed up by concrete personal experience and many episodes that confirm this belief.
It is not necessarily the case that the very first episode in which a decision was made was the most traumatic or the most horrible. The psyche has made some decision “to try it out”, and then a chain of events can be formed that “confirm” the correctness of this decision
the intention to find a real friend goes nowhere, and confusion begins to accumulate in person X until the intention collapses into a point and person X decides: "Real friends just don't exist, that's the law of the universe, to each his own. And I have 742 episodes that clearly confirm that."
Then person X comes to the therapist and says, “Every time - every time! - when I find a person and I start to think he’s a real friend - the same thing happens every time, every time he turns out to be a freak!”
And the therapist replies: “It happens because you have karma like that!” which supposedly explains something.
It turns out that karma is a piling up of traumatic experiences that were once caused by a strong breakup and the acceptance of some unconscious attitude. And further this unconscious attitude begins to program a person for certain behavior, to filter and accumulate similar experiences.
sometimes the amount of emotional charge associated with the affected need becomes unbearable, and it is easier for a person to give up this need or a whole area of life altogether.
In the end, person X decides that there are no friends in this world, at all. You can do anything with people, but it is impossible to be friends with them.
And now person X does not have the category “friendship”, it is blocked by traumatic experiences.
but the intention to have a real friend has not gone anywhere, it can be completed only when person X really has a real friend. And since the intention is not completed, person X wants to have a real friend again and again
and life offers new opportunities: “here, try again, and this time do it right”. If person X had high awareness, he would have done everything right the second time. But, as a rule, person X does not have high awareness, moreover, he has less resources, because part of his attention is stuck in past experiences. And the next time, the same thing happens, maybe even worse and faster.
and life doesn’t stop: “try again… try again…” ![]()
Eventually person X says, “enough, life, leave me alone, I’m not going to be friends with anyone.” Maybe life will leave him alone, and maybe not - still somewhere in the depths of the need remains
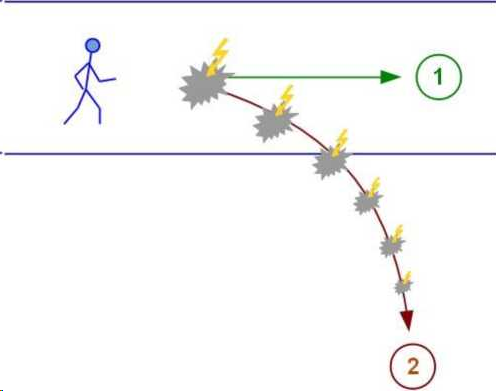
it turns out that a person’s life should have moved to point 1 (see fig.), but went to point 2. If this area of life was connected with some deep need, there is a global gap in life, the person is not what he would like to be, his life path leads in the wrong direction.
from the described model it is clear why events are “garlanded”: all these events are attempts to replay the same situation, attempts to satisfy the same deep need. And as long as this deep need is not satisfied, the attempts will continue.
When many years and many repeated events have passed after the first episode, it is very difficult for a person to understand what need was violated there: the attention will be on recent episodes, and it takes a long time to “dig” to remember what the deep need was in the beginning.
It is necessary to remove many layers of charge in order to understand what kind of need it was, whether it is relevant now, or whether it is just an automatic behavior, a viral program
It is usually not necessary to work through all the episodes of the “garland”: there is one and the same pattern in this entire chain of events, and the setting is most likely the same. It is known from practice: when a person finds this attitude, clearly formulates and realizes it - at that moment the whole chain loses its significance, no matter how many episodes there are.
Recommendations for working with the field
Summary
Take a pen and paper or open a file in your computer.
- Think of a time when you had a traumatic experience. It is best to start with a milder experience, not the strongest.
- Briefly describe on paper or in a file what happened.
- Recall what your expectations were? What went wrong in that episode? What was the discrepancy between your expectation and what actually happened? Write it down.
- Recall how you felt, what were your emotions, body sensations, thoughts - write it all out, unload it all onto paper or a file. Did your state feel like confusion?
- Recall how you came out of this state. What decision, judgment was made? Was it your own decision or was it taken from outside? Write it down.
- Was there another case similar to this one? If yes, work on this case too, starting from point 2.
Work until you have new thoughts, insights, realizations, or until the condition improves.
The field can be played during the process, or it can be turned on after this analysis.
All in your hands. Experiment.
This recommendation is not strict. Customize it for yourself. ![]()
before i saw this i remembered someone said food allergies are traumatic events that stuck in the body. when something shocking happened while eating something for example an apple. then the body is alarmed every time we eat an apple.
but it’s hard to find out what event happened exactly. to replay this episode… is this really necessary to remember the root cause?
from a psychosomatic perspective, the allergen is an “anchor” to which the brain has linked the stressful situation that resulted in the allergy. The information has gone into the subconscious. And in the future, the “anchor” will be the trigger to trigger an allergic reaction. By the way, as I remember, the type of allergen can be used to determine the cause of the allergy.
but I don’t have those charts.
above, I’ve outlined a rough model of how traumas form.
figure out the causes ( trying to ) with a “real” psychologist
Trust the field. ![]()
Definitely slept allot deeper last night after listening . Does the field work better when focusing on the solution for the target issue or is it necessary to focus on what bothers me about target-issue/problem/sensations ect ; also what happens if during the track I end up pondering on multiple issues ? Like if I don’t end up focusing on just one thing for the whole track - I plan on using this pro actively but are there any passive effects from just listening to the field
experiment
focus on 4 components.
Take any problem - think about it, what emotions do you feel? What picture comes to your mind when you think about a problem? what physical sensations? where is the point of the problem?
Or just visualize the problem in volume. ![]()
Often our problems have a cascading principle.
I mean, our experiences are the result of traumas, bad decisions, etc. that you don’t remember at all.
Focus on the present.
or try to find the root of the problem (but this can be difficult at first without practice).
also experiment…
is it acceptable for you to talk through the problems in the process of playing the field? Just focus your attention on something.
Take your time.
save the next conversation for another day. ![]()
Sounds like this is more powerful than the smart tap tapper.
This looks like a real treat! I imagine we could see other field work become much more effective if we use this to tackle the specific blockages related to our goals.
Question: Because this field also goes to work when we are in deep sleep would you advise not listening to overnight playlists immediately following a day where we’ve used this field?
Many thanks!
I would still advise you to continue to follow your established regimen
if you have a specific nightly playlist - use it in your rhythm
If we talk about this field, it activates the necessary processes. I don’t think other fields will interfere with this ![]()
What an interesting field.
I don’t think this replaces my Personal supporter but complements it.
This seems better to act inmediately and in more specfic and diverse situations whereas my Personal is more for generic situations medium/ term even though it’s useful in the shorter time.
Sort of like going to therapy whereas you usually attend for long time.
I’ve just purchased it. Let’s see how it goes.
Update after two weeks. I loop it longer than just twice every day. It’s becoming more and more difficult to focus on things, and situations that I don’t like every day. Less things are bothering me now.
This is indeed better than the smart tap tapper.