Thanks.
Well about 1/3 the weight loss was from “new” or newish weight gain, so it was somewhat easier to lose. (Weight gain due to medication side effects and Hashimotos hypothyroidism- not controlled)
The other 2/3…came off slowly, but steadily.
When I had the last 20-25 lbs left, I plataued for about 1 1/2 years.
Then it finally started to go down again. Like 4-6 lbs/year slowly, the last few years losing 8-10 lbs/yr.
The key is MAINTENANCE, which Ive been on the last 2 years, but even with that still losing slowly, which I’m fine with. I have a weight # I dont want to go below, which is about in 10 lbs. So its been a long haul. Now I’m the healthy size/weight I’ve been most of my adult life, but I got rid of all those clothes! But due to my age (66) everything hangs differently!
(P.S. All this weight loss was “just” from healthy low carb eating and energy expenditure. Plus some of Dream’s fields the last few years. No surgery, no stomach banding or ballooning , no procedures of any kind were done) and no medication.
Patience and persistence.
Actually I have found that if u have a more moderate-severe problem, attacking it in several different ways is very helpful. Again, if its a minor problem probably wont be necessary. Of course u can also start more slowly and “see how it goes”.
does this work with family members
Yes, you can share this field with immediate family members (spouse, parents, kids, siblings).
I listen to Fascia 2 times a day.
I bough this feld week ago.
My results,:
*Better metabolizm🤭
- Slightly firmer skin on my body
- Skin looks more głowy on whole body
I think i will add lymphatic drainage and some automated workout fields.
Ok an update.
I listen 2,3 times a day. After 2 weeks of listening results are:
- Better metabolism. Very regular.

- Firm skin on body. Especially belly area. . It feels like skin is holding all the internal organs in that area.
- Bone structure is more visible. Also on my face.
- Skin has a bit bette, healther r tone
I also use plasma glass skin but i took break to test this field.
I usually drop all my fields when i buy a new one to watch results without any doubs.
I did not exercise or lose weight. Its just this field.
I only did walks and some stretching as usual.
I did not add anything to my self care routine. Its simple nowadays.
Cold showers,coffee peeling, body balm with bergamot and almond oil
I also listen to ojas and vit c when It comes to youth fields.
Other fields on my stack righ t now are golden glow,słow down perception of time,ancestral knowledge, sungazer, brain regeneration, superhuman genius and super human mutant.weath generator, woven world’s millions, probability and alteration.
Congratulations! thats amazing
Thanks.
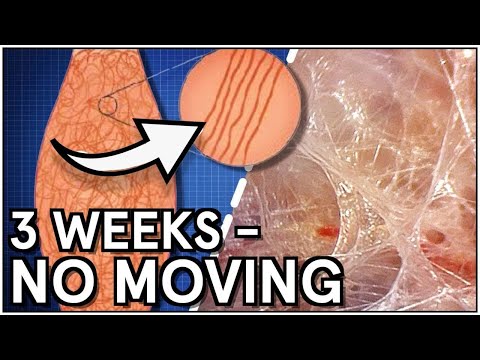
Strolling under the skin: How does it look inside a living body?
The definition of fascia
- Fascia is ONE system, a continuous mesh without beginning and end, that maintains and establishes interconnection, communication and interaction between different parts of the body
- The fascia is the elastic, continous network in the body that extends from the surface of the skin down to each cell and connects to the cell nucleus via the cytoskeleton.
- The fascia is the largest organ, it accounts for more than a third of the ‘musculoskeletal system’ and more correct would be the ‘fasciomusculoskeletal system’. Also pain receptors as well as other nerve receptors are found in the fascia,
Or to quote Jean Claude Guimberteau:
“We thought fascia was nothing, but now we know that it is everything”
Understanding Fascia in 10 minutes – the must see German documentary
In early 2013, a German documentary was broadcast based on the latest research on the Fascia.
Hyaluronic Acid in Inflammation and Tissue Regeneration, 2016
Topics: hyaluronic acid; extracellular matrix; wound healing; Inflammation
Authors: Malgorzata Litwiniuk, Alicja Krejner, Tomasz Grzela
Abstract
Hyaluronic acid (HA), the main component of extracellular matrix, is considered one of the key players in the tissue regeneration process. It has been proven to modulate via specific HA receptors, inflammation, cellular migration, and angiogenesis, which are the main phases of wound healing. Studies have revealed that most HA properties depend on its molecular size. High molecular weight HA displays anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties, whereas low molecular weight HA is a potent proinflammatory molecule. In this review, the authors summarize the role of HA polymers of different molecular weight in tissue regeneration and provide a short overview of main cellular receptors involved in HA signaling. In addition, the role of HA in 2 major steps of wound healing is examined: inflammation and the angiogenesis process. Finally, the antioxidative properties of HA are discussed and its possible clinical implication presented.
How to keep your Fascia healthy and balanced
The best thing to keep yourself healthy and free from injury and thus avoiding getting pain is to try to keep the fascia healthy and make sure the flow and slide and glide works.
- Avoid sitting for too long in the same position, thus changing movements, taking regular breaks from desk work and other undiversified work.
- Avoid excessive strain, monotonous repetitive movements, heavy lifting and twisting, as it can cause micro damage or major muscle and fascia damage and create inflammation and movement restrictions. Elevated lactic acid levels lower the pH of the musculature and fascial system, which can affect and impaired gliding ability.
- Not too much strength training as the concentric workout gives short muscles and thus shorter, tighter fascia. Eccentric training, when the muscles work during extension, provides a smoother and more flexible fascia.
- Varied, healthy diet; Avoid too much sugar as it initiates inflammatory processes and produces a rigid fascia. Also, be careful about other foods that are highly inflammatory and that can trigger the immune system and create autoimmune diseases. Some people are more sensitive than others.
- Take care of the microbes in your gut and intestinal system, eat probiotic supplements, or, for example, acidic products containing lactic acid bacteria, go to the toilet regularly.
- Also avoid prolonged mental stress, which gives high levels of cortisol throughout the day, which has many negative consequences for the body, such as impaired immune system, sleep problems, thin skin and hair loss.
- Sleep well! As we sleep, the body heals and recovers! Sleep deprivation causes stress on the body with many negative factors, high cortisol levels and, among other things, a weakened immune system.
Fascia Lines are the intersections of the body
Fascia lines according to Tom Myers
The basic hypothesis of Thomas Myers’ writings on Fascia kinetic lines is that muscles, no matter what they do individually, also affect tissues throughout the entire body through Fascia based interconnections.
These interconnections can be called Fascia lines and can be followed by the body’s dissectible “meridians” of connective tissue structures. They consist of membranes and ligaments, both superficial and deep connective tissue, loose and tight.
These Fascia lines create stability, resistance, power, flexibility, elasticity, and above all- compensatory posture. So connective tissue structures work in sync, creating a fluid and balanced movement and a posture that maintains balance and direct contact between all body parts.
In Myers book “Anatomy Trains” ligaments are described as the “inner bag” and outside them are Fascia based pathways, lines, interconnected longitudinal structures that distribute power and compensation.
All tissue in the body is naturally linked to the network that the Fascia forms, but these lines are more clearly distinguishable from other tissue and appears to transmit signals / operating with more power through these pathways.
The Fascia consists of many types of collagen, elastin, retinacula fibers, and the sticky proteins called “basal lamina” or also known as the extra-cellular matrix. In this basic substance nutrient exchange and communication between cells and body parts can occur.
You can see that in parts of the body that are blocked, where muscles are locked in either a static mode, or short locked mode and skeletal parts have gotten out of position. Then, the extra-cellular matrix (basal lamina) is thinned and membranes stick together.
The collagen fibers of the Fascia builds up and becomes more stiff and locked from overload / poor mobility. As this occurs, and the basal lamina is also diluted the cells in the area does not get enough nutrition and hydration, and a vicious circle and state of illness is initiated.
The various Fascia lines

Superficial back line / Superficial dorsal line

This line connects and protects the entire rear side as a back shield, from underneath the foot to the top of the skull in two parts. From toes to knees and from the knees to the eyebrows.
When the knees are extended these two parts function as a whole.
The superficial dorsal line prevents fetal position and keeps the body upright and stretched.
We are born huddled together, but with maturity and development the superficial dorsal line and its muscles are strengthened until we have a strong upright position with raised head.
A delicate point along this line is the plantar ligament under the arch of the foot. Problems here are often propagated further up the line. (So treating the foot is very good!)
To always work along the entire superficial dorsal line helps the body towards proper balance and posture.
Superficial front line

This line connects the entire front of the body from the feet to the sides of the skull in two parts. From toes to the pelvis and from the pelvis to the skull.
When the body is upright and the hips stretched the line operates as a whole integrated Fascia.
The function of the movement is to create flexion of the torso and hips, stretch the knees and dorsal flex the foot.
The need to quickly flex up the front of various joints allows this line to contain muscles with more “fast-twitch” fibers.
Here it is also important to examine carefully as the body’s reflex to huddle together and “protect itself” is strong. Traumas can cause lock ups in the superficial front line and treatment of key parts such as the sides of the neck near the ears, front axles, hip flexors and front thighs must be done properly.
This line is often the cause of the forward tilted and rotated pelvis.
Problems after whiplash and neck strain are also quite often located here, in front of the throat which constricts and compresses the cervical spine. (Scalene, sternocleidomastoid)
Lateral line

The lateral line frames both sides of the body from the foot’s center out and inside, it extends along the outside of the leg and thigh. It passes the torso in a zigzag pattern up over the shoulder and attaches close to the ear.
The line’s influence on posture is to balance the front and rear and the lateral right-left.
The line also controls the forces transmitted from other superficial lines, superficial front and back lines, all arm lines and the spiral line.
The lateral line acts to stabilize the torso relative to the legs and helps with the coordination of movement.
The line acts in a side bending manner and lifts the hips and brakes the opposite-side’s rotations and flexions.
Here, problems often occur in the “tibia band” extending on the outside of the hip and thigh. If this part becomes short and stiff it affects the hip movement negatively and movement that is supposed to be taken with the hip will instead affect the lower back by excessive lateral movement. Many times poor mobility and numbness in the thigh’s and hip’s outside can cause back pain.
Spiral line

The spiral line creates a loop around the body in two opposite circles, to the right and left. It combines each side of the skull, crosses the thoracic spine back to the opposite shoulder. Then, it goes around the chest to the front to cross the navel and goes down to the hip.
From the hip the spiral line runs like a jump rope down the outside of the front thigh down to the outside of the foot. It makes a loop under the foot, continues up again towards the outer thigh more towards the rear side of the ischium. Further, onward they cross again and merge into the erector spinaes fascia.
This line stabilizes the body in all planes through its double enclosing loop. It connects the foot with the pelvis and is important in the regulation of the knee position when we walk.
When bothered this line causes rotations and imbalances throughout the body.
Fascia Arm Lines
Below are four distinct Myofascial meridians that run from the axial skeleton through four different planes in the shoulder, along all sides of the arm and to the hand out to the thumb, little finger, palm and back of the hand.
Superficial Back Arm Line & Superficial Front Arm Line

Deep Back Arm Line & Deep Front Arm Line

The arm lines have more cross-over structures than there are in the legs. So even if this describes longitudinal structures, they are bound together transversely as well.
This is because human arms are built to have high mobility compared to the legs that offer more stability.
To cope with this free movement more varied lines and support in all directions is required.
The arm lines is quite logically arranged with a deep and a shallow line on the front of the arm, as well as a deep and shallow one on the back of arm.
The arm lines are named after their location where they cross the shoulder. All arm lines goes unnoticed into all other lines and performs pushing, pulling, rotations, anvils and infinite movements in collaboration with the eyes in order to perform all the advanced movements we do with our arms and hands.
Functional lines

The functional lines emanate from the arm lines and cross the torso towards the opposite outer side of the pelvis and legs. Or you can say that the route goes from the opposite side as they do not have a direction.
One of the lines crosses the front and one crosses the back, so that together they form an X on both the front and backside. A third line of this group is the ipsilateral functional line, which runs from the shoulder to the inside of the same side’s knee.
These lines are activated primarily through active exercise as in sports that require a bit more stabilization, counterweight, or getting power from your opposite side.
An example is a powerful baseball throw where the thrower draws strength from the ground and then pushes power up diagonally to the throwing hand, or a tennis player’s backhand.
These lines are less active in the standing position.
Deep front line

The deep front line is located between the right and left lateral lines in the front plane, wedged between the superficial front line and superficial dorsal line in the sagittal plane. It is surrounded by the spiral lines and functional lines.
The deep front line includes the body’s Myofascial “core”. If we start from the bottom the line has deep roots under the foot, passing up the skeleton of the back leg, behind the knee and inner thigh. From here, a larger track runs through the hip, pelvis and lumbar vertebrae front while an alternative pathway runs along the back of the thigh to the pelvic floor after which it returns with the first part at the lumbar vertebrae.
Further upward through the diaphragm the deep front line passes up through the chest with many branches through the thoracic viscera and ends on the bottom of both the neuro cranium and the visceral cranium.
This line is the most three-dimensional in shape rather than a line. All lines are of course partly three-dimensional, but they are more like power transmission lines.
The deep front line definitely takes up more space than other lines. In the legs the deep front line envelops most of the stabilizing muscles. Through the hip the line has a close relation to the hip joint and synchronizes the rhythm of our walk with the rhythm of our breathing.
In the torso the deep front line along with the autonomic ganglia, runs between our neuromotor chassis and the organs that supports cells in the ventral chest cavity.
In the neck the deep frontal line provides counterbalance to the pulling mechanisms that the superficial front and back line causes.
An in-depth understanding of this line is essential for the successful treatment in almost all types of manual techniques and therapies.
Training for strengthened Fascia
Exercise increases collagen production in tendons, ligaments and all Fascia. To stimulate collagen formation in tendons and ligaments, it doesn’t matter if the exercise is eccentric (muscle contraction during extension) or concentric (muscle contraction during shortening).
To stimulate lysyl oxidase in a tendon, it also doesn’t matter much if the training is eccentric, concentric or isometric (static). Regardless of the work performed, the tendon is subjected to a pull.
In musculature, on the other hand, eccentric (and also static) training generally provides a more effective stimulation of collagen and lysyl oxidase with several factors, than concentric. Hence, it is more effective with eccentric or static exercises for the muscles.
Strength training should be done slowly to get a smoother Fascia. The slow training breaks crosslinks and makes collagen smoother. Too fast training can cause stiff tendons and Fascia.
Training to strengthen or heal, for example, a tendon, does not have to be so heavy. There must be the right load for the type of tissue, ie stretching of tendons, ligaments so that the cells are “pulled out”. This stimulates the formation of mainly collagen type I and lysyl oxidase. Maximum stimulation of the cells takes place after 5-10 minutes, then not much more occur! Now the cells must recover for at least 6 hours before they are ready for new stimulation.
If you have an injured tendon it is important that it is stretched slowly and statically, about 30 seconds. Then the healthy fibers relax, and the force is transferred to the damaged area where the cells receive a signal to start forming new collagen. Dynamic stretch in that case means that the healthy fibers take all the stress and protect the damaged area, and the cells do not receive any stimulus, nothing that promotes healing. This is called stress shielding.
Articular cartilage is stimulated by dynamic compression, which stimulates the synthesis of collagen II. Thus, new articular cartilage formation is stimulated by dynamic training, such as jump rope.
Evidence-based training advice for strengthening tendons and ligaments;
Add extra workouts to strengthen connective tissue / fascia and avoid injury.
- This type of training session should be less than 10 minutes of activity, aimed at particularly exposed tendons / ligaments depending on the sport. For example, running athletes should focus on strengthening the hamstrings, knees and Achilles tendon.
- The training can possibly be performed with light weight and a limited range of motion. This extra training should be performed 6 hours before or after another training! The cells must have recovered and be able to receive the stimulus!
Rehab of tendon / ligament injury;
-
After an injury, training should start as soon as possible. The training can consist of simple range of motion exercises and little load as the load amplitude is not important to stimulate collagen production. The training should last less than 10 minutes, followed by 6 hours of “rest”. This means 3 short training periods per day. An injured tendon should be stretched statically for about 30 seconds with several repetitions during 5 to 10 minutes.
-
Eat protein rich in the amino acid leucine (essential amino acid, found in meat and dairy products). For athletes or during rehab, supplements can be taken. It strengthens the muscles, which is also good for the durability of the tendons.
-
Take a supplement of 15 g of hydrolysed collagen or gelatin before training, together with vitamin C. It is needed for collagen formation in fascia, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, bone tissue etc. Which type of collagen is not important. The cells produce the right type for the tissue depending on the mechanical force.
-
These nutritional supplements should be taken in close proximity before the targeted exercise, 30 – 60 minutes before, when the blood flow to the tendons and ligaments is poor but increases during exercise, which increases the nutrient uptake into the tissue. Then it is important that the nutrition is available right then!
Such detailed information ! Thank you so much!
I’ve bought this field last week and I can definitely see that my body tissues are more firm, and that in just 3 days of listening! Wow, I’m impressed!
Bump 
we’re gonna take this up a level 
This work for loose skin in all the body?
Indeed.
Thanks buddy
Has anyone experienced tightening/lifting of the fascia in the face from this? I’ve seen a few comments but curious about people’s experience with this now that more has passed!