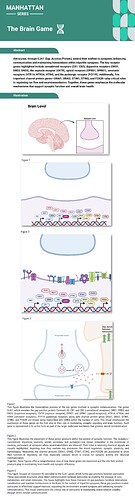
Firstly, let’s understand some neurology.
Simple explanations of used terms:
Astrocytes
Astrocytes are a type of glial cell found in the brain and spinal cord. They are star-shaped cells that play important roles in maintaining the health and function of the nervous system.
Astrocytes have a number of functions, including:
- Providing structural support: Astrocytes help to maintain the structural integrity of the brain and spinal cord by providing a scaffold for other cells to grow on.
- Regulating blood flow: Astrocytes help to regulate blood flow in the brain by constricting or dilating blood vessels in response to changes in neural activity.
- Regulating neurotransmitters: Astrocytes play an important role in regulating the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain. They take up neurotransmitters that are released by neurons and convert them into a form that can be recycled or eliminated.
- Maintaining the blood-brain barrier: Astrocytes help to maintain the blood-brain barrier, a specialized layer of cells that separates the blood from the brain. This helps to protect the brain from harmful substances that may be present in the blood.
- Repairing damaged tissue: Astrocytes can differentiate into different types of cells and play a role in repairing damaged tissue in the brain and spinal cord.
Astrocyte’s endfeet
Astrocyte endfeet are specialized structures found at the ends of astrocyte processes that come into contact with blood vessels in the brain. These structures are sometimes referred to as perivascular endfeet or vascular endfeet.
Astrocyte endfeet are important for a number of reasons. First, they help to form the blood-brain barrier by creating a physical barrier between the blood vessels and the brain tissue. This barrier helps to protect the brain from harmful substances that may be present in the blood.
In addition to forming the blood-brain barrier, astrocyte endfeet also play a role in regulating blood flow in the brain. They can constrict or dilate blood vessels in response to changes in neural activity, which helps to ensure that the brain receives an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients.
Astrocyte endfeet also play a role in removing waste products from the brain. They take up excess neurotransmitters and other substances that are no longer needed and transport them to the blood vessels for removal from the brain.
Synaptic clefts
Synaptic clefts are the small gaps or spaces that exist between two neurons at a synapse. When an action potential reaches the end of a presynaptic neuron, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters, which diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, transmitting the signal from one neuron to another.
The synaptic cleft is a crucial component of synaptic transmission, as it allows for precise control and modulation of neuronal communication. The width of the synaptic cleft is typically around 20-40 nanometers, and it contains a number of proteins and other molecules that help to regulate the release, diffusion, and uptake of neurotransmitters.
The function of the synaptic cleft is highly dynamic, and it can be influenced by a number of factors, including the strength and frequency of neuronal activity, the availability of neurotransmitters, and the presence of neuromodulators and other signaling molecules.
Tripartite synapses
Tripartite synapses are a type of synapse that involve not only the traditional pre- and postsynaptic neurons, but also a third component: astrocytes. In tripartite synapses, astrocytes form direct physical contacts with both the pre- and postsynaptic neurons, allowing them to play an active role in regulating synaptic transmission.
Astrocytes can release and take up neurotransmitters, modulate the strength of synaptic connections, and provide metabolic support to neurons. They can also influence synaptic plasticity and participate in homeostatic processes that help to maintain the balance of activity in neural circuits.
The concept of tripartite synapses has been the subject of much research in recent years, and there is growing evidence to suggest that these synapses play an important role in a range of neurological processes, including learning and memory, development and plasticity of neural circuits, and the response to injury and disease.
Intercellular gap junctions
Intercellular gap junctions are specialized channels that allow for direct communication and exchange of ions and small molecules between neighboring cells. These channels are formed by connexins, a family of transmembrane proteins that are expressed in a variety of tissues and cell types.
Gap junctions are important for a number of physiological processes, including the coordination of cardiac and smooth muscle contractions, the synchronization of neuronal activity, and the regulation of metabolic and homeostatic processes.
In the nervous system, gap junctions play a critical role in the propagation of electrical signals and the synchronization of neuronal activity. Gap junctions between neurons are typically found in regions where high-frequency electrical signals are generated, such as in the thalamus and the cerebellum.
Gap junctions can also be found between neurons and glial cells, such as astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. These intercellular connections allow for rapid and coordinated communication between different cell types, which is important for processes such as myelination and the regulation of synaptic activity.
Which compounds might be in (EDIT: but are not):
List of beneficial substances/compounds for the mentioned goals
-
Omega-3 fatty acids: These compounds have been shown to enhance the development and function of astrocytes, as well as improve intercellular communication and synaptic plasticity.
-
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC): NAC is an antioxidant and a precursor to glutathione, a molecule that is important for the regulation of neurotransmitters and protection against oxidative stress. NAC has been shown to enhance dopaminergic and serotonergic signaling, as well as improve gap junction function.
-
Oxytocin: Oxytocin is a neuropeptide that is involved in social bonding, trust, and stress regulation. Studies have shown that oxytocin can enhance synaptic plasticity and improve cognitive function, as well as increase the formation of gap junctions.
-
Resveratrol: Resveratrol is a polyphenol found in grapes, berries, and other plants. It has been shown to enhance neuronal plasticity and improve intercellular communication, as well as increase the levels of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin.
-
Magnesium: Magnesium is an essential mineral that is important for a range of physiological processes, including the regulation of electrical signaling in neurons. Studies have shown that magnesium can improve synaptic plasticity and enhance intercellular communication, as well as reduce the risk of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
-
Cytokines: Certain cytokines, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), are involved in the regulation of neuronal growth, plasticity, and survival. Supplementation with these cytokines or compounds that enhance their production may be able to improve neurological function.
-
Glutamate: Glutamate is an important neurotransmitter that is involved in the regulation of synaptic transmission and plasticity. It has been shown to be involved in the formation of tripartite synapses.
-
Calcium: Calcium is a key signaling molecule that is involved in the regulation of synaptic transmission and plasticity. It has been shown to be involved in the formation and maintenance of tripartite synapses.
-
Dopamine: Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is involved in reward, motivation, and movement. It has been shown to modulate the formation and function of tripartite synapses.
-
Serotonin: Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that is involved in mood, appetite, and sleep. It has been shown to modulate the formation and function of tripartite synapses.
-
Omega-6 fatty acids: Omega-6 fatty acids, like omega-3 fatty acids, are essential fatty acids that are important for brain health. Some studies have suggested that omega-6 fatty acids may also play a role in the regulation of astrocyte function and the formation of tripartite synapses, but more research is needed to fully understand this relationship.
-
Growth factors: Various growth factors, such as fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) and epidermal growth factor (EGF), have been shown to enhance astrocyte function and promote the formation of tripartite synapses.
-
Neuromodulators: Neuromodulators like acetylcholine, norepinephrine, and histamine have been shown to modulate astrocyte function and influence the formation of tripartite synapses.
-
Antioxidants: Antioxidants, such as vitamin E, vitamin C, and glutathione, have been shown to protect astrocytes from oxidative stress and promote their function, which may ultimately lead to enhanced tripartite synapse formation.
-
Curcumin: Curcumin is a natural compound found in turmeric that has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Some studies suggest that curcumin may enhance astrocyte function and promote the formation of tripartite synapses.
-
Cannabidiol (CBD): CBD is a non-psychoactive compound found in the cannabis plant. It has been shown to have neuroprotective properties and may enhance astrocyte function and promote the formation of tripartite synapses.
-
Bacopa monnieri: Bacopa monnieri is a traditional herbal medicine used to enhance cognitive function. It has been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, and may enhance astrocyte function and promote the formation of tripartite synapses.
Possibly even these:
-
Lion’s mane mushroom: Lion’s mane mushroom contains compounds called erinacines and hericenones, which have been shown to stimulate nerve growth factor (NGF) production in the brain. NGF is important for the growth and maintenance of neurons and may help enhance cognitive function.
-
Ginkgo biloba: Ginkgo biloba is a traditional herbal medicine that has been shown to improve cognitive function, particularly in elderly individuals. It may also enhance blood flow to the brain and protect against oxidative damage.
-
Bacillus subtilis: Bacillus subtilis is a type of bacteria that has been shown to improve cognitive function and enhance memory formation in animal studies. It may also have anti-inflammatory properties.
-
L-theanine: L-theanine is an amino acid found in green tea that has been shown to have a calming effect on the brain. It may also enhance cognitive function and improve attention and focus.
-
Phosphatidylserine: Phosphatidylserine is a type of phospholipid that is important for the structure and function of cell membranes. It may enhance cognitive function and improve memory, particularly in elderly individuals.
![]()